I previously wrote this article in my blog, Think Big!.
Overview
This lesson focuses on how to send mail messages in .NET Framework via a SMTP server. It firstly discusses the techniques which .NET Framework provides you to send mail messages. After that, it discusses types available for you when working with SMTP servers. Next, it discusses how to implement these techniques and to send mails from a .NET client.
Attached with the article a sample application, Geming Mail+, which is used to send mails from a various SMTP servers. This application is open-source, so you can download its code freely.
Introduction
Simple Mail Transport Protocol or simply SMTP provides a way for applications to connect to the mail server and send mail messages via server's exposed SMTP service.
Before .NET 2.0, you were to access SMTP via classes in System.Web.Mail namespace which resides in System.Web.dll library. With the release of .NET 2.0, System.Web.Mail classes became deprecated and replaced with classes in System.Net.Mail namespace which exists in System.dll library. That means that you still can use classes of System.Web.Mail, however, you will receive warnings indicate that those classes are deprecated and you should use classes from System.Net.Mail namespace.
Type Overview
System.Net.Mail Types
System.Net.Mail namespace includes many types each of which provides a special feature. In fact, the most time you will not need to use all of them or to know them at all. However, being aware of what .NET provides to you for accessing SMTP is better to help you evolving your SMTP client application in many sides and in various degrees. Here are the most common classes of System.Net.Mail:
- SmtpClient:
One of the essential classes provides you with means of connecting to the SMTP server and sending mail messages. Before starting using this class and send a message, you must initialize server properties like Host, Port, and EnableSsl to allow communicating with the SMTP server. SmtpClient also provides you with some methods like the Send method that sends a specific message synchronously, and SendAsync to send it asynchronously.
- MailMessage:
The message to be sent using the SmtpClient class. This class exposes many properties specific to the message like To, CC, Bcc, Subject, and Body properties that corresponds to the message fields.
- MailAddress:
Encapsulates a mail address. Provides the DisplayName and Address properties.
- MailAddressCollection:
A collection of MailAddress objects. This collection is used inside the MailMessage object in the properties To, CC, and Bcc.
- Attachment:
Encapsulates an attached file.
- AttachmentCollection:
A collection of Attachment objects. Used in the MailMessage class in its Attachments property.
- SmtpException:
Represents an exception thrown from the SmtpClient if it failed to send a message. Use SmtpException's StatusCode property to determine the error occurred. In addition, see the inner exception for more details.
- SmtpFailedRecipientException and SmtpFailedRecipientsException:
Represent exceptions thrown when the SmtpClient fails to send a message to a specific recipient or a group of recipients. Both classes are derived from SmtpException.
- SmtpPermission and SmtpPermissionAttribute:
If you are aware of your code running from various locations or from an unsecure environment, you can use these classes to control how your application should access SMTP servers. You use SmtpPermission to control application permissions imperatively. SmtpPermissionAttribute is used to control the permissions declaratively. Consult MSDN documentation for more information about these types and how to use them.
In addition, System.Net.Mail includes various enumerations each represents a set of options for a specific feature. For example, MailPriority enumeration is exposed via the Priority property of a MailMessage object; it can take one of three values, Low, Normal, and High, and it is used to mark your message with a specific priority flag.
System.Web.Mail Types
Besides types in System.Net.Mail, for whose interested in .NET 1.0 and descendent before .NET 2.0, we will cover types of System.Web.Mail briefly. In fact, they are very few types, actually, they are only three classes and three enumerations, and they serve the same as types in System.Net.Mail.
Classes in System.Web.Mail:
- SmtpMail:
Serves the same as System.Net.Mail.SmtpClient. However, it exposes only a single property SmtpServer. Plus, it exposes methods for sending mail messages.
- MailMessage:
Encapsulates message related information and data like To, CC, BCC, Subject, and Body fields.
- MailAttachment:
Encapsulates an attachment. MailMessage exposes a list of MailAttachment objects via its Attachments property.
Besides those only three classes, System.Web.Mail also includes three enumerations, MailEncoding, MailFormat, and MailPriority. I think that those enumerations have expressive names enough and do not need to be explained. If you need some explanation consult MSDN documentation or continue reading this article. Although, this article concentrates on types from System.Net.Mail, they are very similar to the types in System.Web.Mail.
SMTP Servers
In order to connect to a SMTP server you need to be aware of four things:
- Server address:
Like smtp.example.com.
- Port number:
Usually 25, and sometimes 465. Depends on server's configuration.
- SSL:
You need to know if the server requires a SSL (Secure Socket Layer) connection or not. To be honest, most servers require SSL connections.
- Credentials:
You need to know if the server accepts default credentials of the user or requires specific credentials. Credentials are simply the username and password of the user. All e-mail service providers require specific credentials. For example, to connect to your Gmail's account and send mails via Gmail's SMTP server, you will need to provide your mail address and password.
The following is a list of some of the major e-mail service providers who provide SMTP services for their clients:
| Name |
Server Address |
Port |
SSL Required? |
| Live |
smtp.live.com |
25 |
Yes |
| Gmail |
smtp.gmail.com |
25 or 465 |
Yes |
| Yahoo! |
plus.smtp.mail.yahoo.com |
465, 25, or 587 |
Yes |
| Only for Plus! accounts. Consult Yahoo! documentation for more help about selecting the right port number. |
| GMX |
mail.gmx.com |
25 |
No |
Implementation
The following is a simple code segment uses classes from System.Net.Mail namespace to send mail messages via GMX's SMTP server.
Visit GMX; one of the leader internet mail service providers.
Do not forget to add a using statement (Imports in VB.NET) for the System.Net.Mail namespace.
// C# Code
MailMessage msg = new MailMessage();
// Your mail address and display name.
// This what will appear on the From field.
// If you used another credentials to access the SMTP server, the mail message would be
// sent from the mail specified in the From field on behalf of the real sender.
msg.From = new MailAddress("[email protected]", "Example");
// To addresses
msg.To.Add([email protected]);
msg.To.Add(new MailAddress("[email protected]", "Friend A"));
// You can specify CC and BCC addresses also
// Set to high priority
msg.Priority = MailPriority.High;
msg.Subject = "Hey, a fabulous site!";
// You can specify a plain text or HTML contents
msg.Body = "Hello everybody,<br /><br />" +
"I found an interesting site called <a href=\"http://ThinkBig.it.tc\">" +
"Think Big!</a>. Be sure to visit it soon.";
// In order for the mail client to interpret message body correctly,
// we mark the body as HTML because we set the body to HTML contents.
msg.IsBodyHtml = true;
// Attaching some data; throws an exception if the file does not exist
msg.Attachments.Add(new Attachment("C:\\Site.lnk"));
// Connecting to the server and configuring it
SmtpClient client = new SmtpClient();
client.Host = "mail.gmx.com";
client.Port = 25;
client.EnableSsl = false;
// The server requires user's credentials not the default credentials
client.UseDefaultCredentials = false;
// Provide your credentials
client.Credentials = new System.Net.NetworkCredential("[email protected]", "buzzwrd");
// Use SendAsync to send the message asynchronously
client.Send(msg);
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
' VB.NET Code
Dim msg As New MailMessage()
' Your mail address and display name.
' This what will appear on the From field.
' If you used another credentials to access the SMTP server, the mail message would be
' sent from the mail specified in the From field on behalf of the real sender.
msg.From = New MailAddress("[email protected]", "Example")
' To addresses
msg.To.Add([email protected])
msg.To.Add(New MailAddress("[email protected]", "Friend A"))
' You can specify CC and BCC addresses also
' Set to high priority
msg.Priority = MailPriority.High
msg.Subject = "Hey, a fabulous site!"
' You can specify a plain text or HTML contents
msg.Body = "Hello everybody,<br /><br />" & _
"I found an interesting site called <a href=""http://ThinkBig.it.tc"">" & _
"Think Big!</a>. Be sure to visit it soon."
' In order for the mail client to interpret message body correctly,
' we mark the body as HTML because we set the body to HTML contents.
msg.IsBodyHtml = True
' Attaching some data; throws an exception if the file does not exist
msg.Attachments.Add(New Attachment("D:\Site.lnk"))
' Connecting to the server and configuring it
Dim client As New SmtpClient()
client.Host = "mail.gmx.com"
client.Port = 25
client.EnableSsl = False
' The server requires user's credentials not the default credentials
client.UseDefaultCredentials = False
' Provide your credentials
client.Credentials = New System.Net.NetworkCredential("[email protected]", "buzzwrd")
' Use SendAsync to send the message asynchronously
client.Send(msg)
|
Changing Mail Delivery Method
You can specify that messages sent do not go to the SMTP server. Instead, it is sent to a directory in your computer that you specify. Actually, it is a good idea when it comes to testing your application. Thus, decreases the testing time.
SmtpClient supports two properties for changing mail delivery location; they are DeliveryMethod and PickupDirectoryLocation properties. DeliveryMethod specifies the delivery method that would be taken when sending the message. This property is of type SmtpDeliveryMethod enumeration; therefore, it can be set to one of three values:
- Network: (default)
The message is sent via the network to the SMTP server.
- PickupDirectoryFromIis:
The message is copied to the mail default directory of the Internet Information Services (IIS).
- SpecifiedPickupDirectory:
The message is copied to the directory specified by the property PickupDirectoryLocation.
The following lines change the delivery location to a specific location in the drive C. You can add the following lines before the line that calls Send() method of the SmtpClient.
In order for the example to run correctly, the specified directory must be existed or you will receive an exception when executing the Send() method.
// C# Code
client.DeliveryMethod = SmtpDeliveryMethod.SpecifiedPickupDirectory;
client.PickupDirectoryLocation = "C:\\mails";
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
' VB.NET Code
client.DeliveryMethod = SmtpDeliveryMethod.SpecifiedPickupDirectory
client.PickupDirectoryLocation = "C:\mails"
|
A Sample Application
Attached with the article, Geming Mail+, an application that is used to send mails via extendable variety of SMTP servers. This application created using .NET 2.0 and Visual Studio 2008. The following are snapshots of the application:

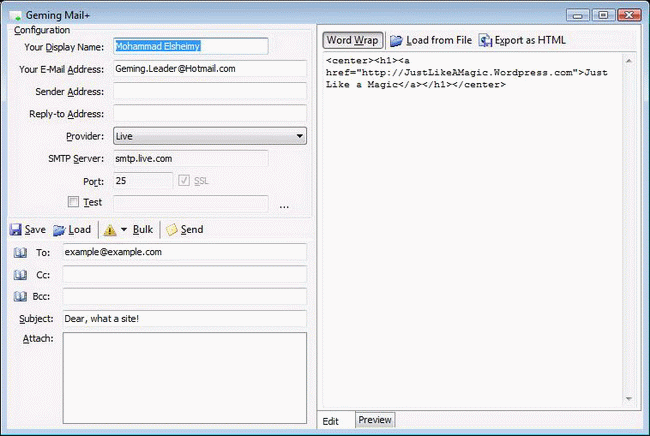
Summary
This lesson was a great introduction to e-mail programming in .NET Framework. You learned how to send mails via a SMTP server. Soon we will cover how to receive mails in .NET Framework.
Have a nice day...