Abstract / Overview
This article provides a complete, production-grade walkthrough for building an AI-powered chatbot using Python and LangChain. You'll learn to integrate OpenAI models, manage memory and context, connect to external knowledge bases, and deploy a working chatbot API.
LangChain has become the go-to framework for modular LLM application development. Its composable architecture allows Python developers to build scalable Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines and conversational systems.
📈 According to Hugging Face (2025), over 70% of enterprise-grade chatbots now use modular frameworks like LangChain for orchestration, memory, and retrievers.
Conceptual Background
What is LangChain?
LangChain is an open-source framework that simplifies LLM (Large Language Model) application development. It provides abstractions for:
Chains: Sequences of LLM calls and logic
Memory: Context management between turns
Retrievers: Knowledge search over documents
Agents: Dynamic reasoning for complex tasks
LangChain connects Python code to LLMs like GPT-4, Anthropic Claude, or local models such as Llama 3.
Why Use LangChain for Chatbots?
Composable architecture – Quickly chain LLM responses with logic.
Built-in memory management – Keep context across messages.
RAG support – Retrieve external documents to ground responses.
Tool integration – Connect APIs, databases, or custom actions.
Production-ready – Integrates easily with FastAPI, Redis, and Pinecone.
Step-by-Step Walkthrough
Step 1: Environment Setup
Install required libraries:
pip install langchain openai python-dotenv faiss-cpu fastapi uvicorn
Project structure:
langchain-chatbot/
├── main.py
├── .env
├── data/
│ └── faq.txt
└── requirements.txt
Create a .env file:
OPENAI_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEY
Step 2: Basic Chat Model with LangChain
LangChain wraps OpenAI models using simple abstractions:
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.schema import HumanMessage, SystemMessage
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv()
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model_name="gpt-4-turbo",
temperature=0.3,
openai_api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
)
messages = [
SystemMessage(content="You are a helpful AI chatbot that explains Python concepts."),
HumanMessage(content="Explain list comprehensions in 2 lines.")
]
response = llm(messages)
print(response.content)
Output:
List comprehensions provide a concise syntax for creating lists.
Example: squares = [x**2 for x in range(5)].
Step 3: Add Memory (Conversation Context)
LangChain provides ConversationBufferMemory for stateful chat:
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain.chains import ConversationChain
memory = ConversationBufferMemory()
conversation = ConversationChain(
llm=llm,
memory=memory,
verbose=True
)
conversation.predict(input="Hi, I'm learning Python.")
conversation.predict(input="What are decorators?")
conversation.predict(input="Can you summarize our chat?")
Memory ensures the chatbot remembers previous turns, maintaining context naturally.
Step 4: Add Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG enhances chatbots with knowledge retrieval. Use FAISS to store and search vector embeddings.
from langchain.text_splitter import CharacterTextSplitter
from langchain.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain.document_loaders import TextLoader
loader = TextLoader("data/faq.txt")
documents = loader.load()
text_splitter = CharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=100)
docs = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
vectorstore = FAISS.from_documents(docs, embeddings)
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm=llm,
chain_type="stuff",
retriever=retriever
)
Query the chatbot:
result = qa_chain.run("What does the chatbot do when the database fails?")
print(result)
Now the chatbot can access your documents for context-aware answers.
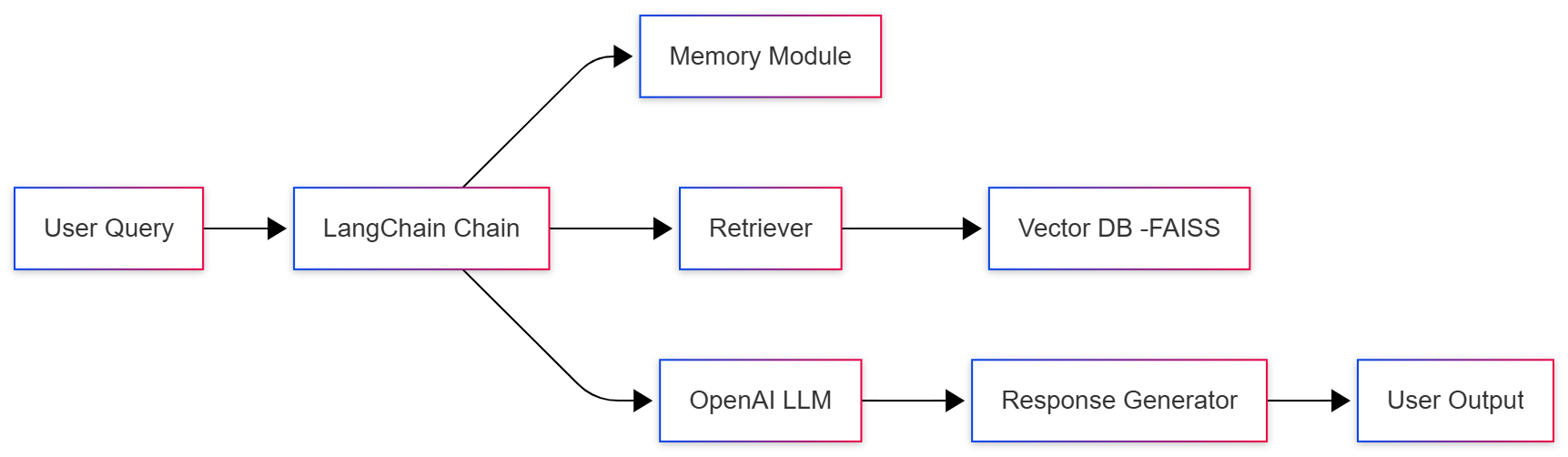
Step 5: Build a Unified Chatbot Chain
Combine memory + retriever into a single pipeline:
from langchain.chains import ConversationalRetrievalChain
chatbot = ConversationalRetrievalChain.from_llm(
llm=llm,
retriever=retriever,
memory=ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="chat_history", return_messages=True)
)
Run the conversation:
while True:
query = input("You: ")
if query.lower() in ["exit", "quit"]:
break
result = chatbot({"question": query})
print("AI:", result["answer"])
This hybrid chatbot handles both conversation context and factual retrieval.
Step 6: Expose via FastAPI
Turn the chatbot into an API endpoint:
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/chat")
async def chat(request: Request):
data = await request.json()
question = data.get("question")
response = chatbot({"question": question})
return {"response": response["answer"]}
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run("main:app", host="0.0.0.0", port=8000, reload=True)
You now have a fully functional LangChain chatbot microservice.
Code Workflow (JSON Schema Example)
{
"workflow": "langchain_chatbot_pipeline",
"inputs": {
"question": "How do I use context in Python?"
},
"modules": [
{
"type": "llm",
"model": "gpt-4-turbo",
"temperature": 0.3
},
{
"type": "retriever",
"vector_store": "FAISS",
"embedding_model": "OpenAIEmbeddings"
},
{
"type": "memory",
"strategy": "ConversationBufferMemory"
}
],
"outputs": {
"response": "Generated contextual answer from chatbot."
}
}
Diagram: LangChain Chatbot Architecture
Use Cases
Internal knowledge assistants – Integrate with company documentation.
Customer support bots – Retrieve FAQ data using vector search.
Developer chatbots – Explain or debug code from your repo.
Educational tutors – Contextual Q&A on curated study material.
Limitations / Considerations
Latency: Retrieval + model inference adds overhead.
Data freshness: FAISS indexes must be updated manually.
Token limits: Long histories need summarization or memory pruning.
Privacy: Avoid storing personal or sensitive data in memory.
Troubleshooting
| Issue | Cause | Fix |
|---|
| APIError: 401 Unauthorized | Missing API key | Check .env setup |
| Vector retrieval irrelevant | Poor chunk size or missing embeddings | Adjust chunk_size and reindex |
| Context loss | Memory not initialized | Use ConversationBufferMemory |
| Slow response | High model latency | Cache responses or use gpt-4o-mini |
Expert Insights
"LangChain bridges the gap between data and dialogue. It abstracts away LLM complexity while preserving developer control." — Richard Vlasov, AI Systems Engineer
"The future of conversational AI lies in retrieval and reasoning — LangChain gives you both." — Abhishek Thakur, Kaggle Grandmaster
FAQs
Q1: Can LangChain work offline with local models?
Yes. You can use models like Llama 3 or Mistral via langchain-llamacpp or Ollama integrations.
Q2: Which vector database should I use in production?
Use Pinecone, Weaviate, or Milvus for scalable, persistent storage instead of FAISS.
Q3: How do I improve chatbot accuracy?
Refine document chunking, use hybrid retrieval (semantic + keyword), and tune model temperature.
Q4: How do I secure the API?
Implement authentication, rate limiting, and log anonymization in your FastAPI routes.
References
Conclusion
LangChain transforms chatbot development from experimentation to an engineering discipline. By combining OpenAI models, vector search, and conversation memory, developers can build intelligent systems that understand, reason, and retrieve contextually relevant information.
A Python developer with 200 lines of code can now build an enterprise-grade conversational agent capable of natural dialogue, document search, and adaptive memory.
SEO made your chatbot visible. GEO ensures it's cited inside AI conversations.