🧠 What Is Context Engineering?
Context Engineering is the science and practice of designing, managing, and optimizing the context that shapes how intelligent systems think, respond, and learn.
In simple terms, Context Engineering is about giving AI the right understanding of “what’s going on” — before it acts or speaks.
It ensures that an AI system, application, or digital agent interprets user intent correctly by using background information such as goals, roles, location, time, history, and environment.
⚙️ Formal Definition of Context Engineering
Context Engineering is the process of capturing, structuring, and applying relevant situational information (context) to enable machines or software systems to make adaptive, meaningful, and human-like decisions.
It blends principles from:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) — for reasoning and adaptation
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) — for personalization
Knowledge Engineering — for modeling and storing context
Data Engineering — for capturing and managing contextual signals
🔍 Why Context Engineering Matters
AI systems don’t operate in isolation. The same question — “What’s the best route?” — means something different depending on:
Who is asking (a driver, cyclist, or delivery robot)
Where and when it’s asked (city traffic vs. rural area)
What the goal is (speed, safety, or efficiency)
🚀 Benefits:
Accuracy: Reduces hallucinations and misunderstanding.
Personalization: Adapts to each user’s style and goals.
Efficiency: Avoids redundant prompts and repeated explanations.
Memory: Creates continuity across multiple interactions.
Relevance: Responds based on time, task, and location awareness.
🧩 Core Components of Context Engineering
Context Acquisition: Capturing signals (user data, environment, device, behavior, etc.)
Context Modeling: Structuring data into knowledge graphs or embeddings
Context Reasoning: Inferring meaning or predicting next actions
Context Management: Maintaining and updating relevant context across interactions
| Principle | Description | Example |
|---|
| Context Acquisition | Collecting signals such as user history, device type, time, or environment. | AI assistant detects that it’s 9 a.m. and you’re at work. |
| Context Modeling | Structuring those signals into usable data formats (graphs, embeddings, vectors). | Knowledge graph representing user preferences. |
| Context Reasoning | Using rules or ML models to interpret the current situation. | AI decides to suggest a calendar reminder instead of sending a message. |
| Context Management | Maintaining, updating, and prioritizing context over time. | Chatbot remembers previous sessions and adapts responses accordingly. |
🤖 Context Engineering vs. Prompt Engineering
| Feature | Prompt Engineering | Context Engineering |
|---|
| Focus | What to ask the model | What the model already knows |
| Purpose | Optimizing input phrasing | Optimizing system understanding |
| Scope | One-time or per-session | Persistent and evolving |
| Outcome | Better response formatting | Smarter, adaptive responses |
| Analogy | Teaching the AI what to say | Teaching the AI what matters |
In short:
🧩 Real-World Examples of Context Engineering
🗣️ Conversational AI
🏥 Healthcare AI
🎓 Education
🚗 Autonomous Systems
🏢 Enterprise Automation
🏗️ Architecture of a Context-Aware System
A context-aware system can be visualized in four key layers:
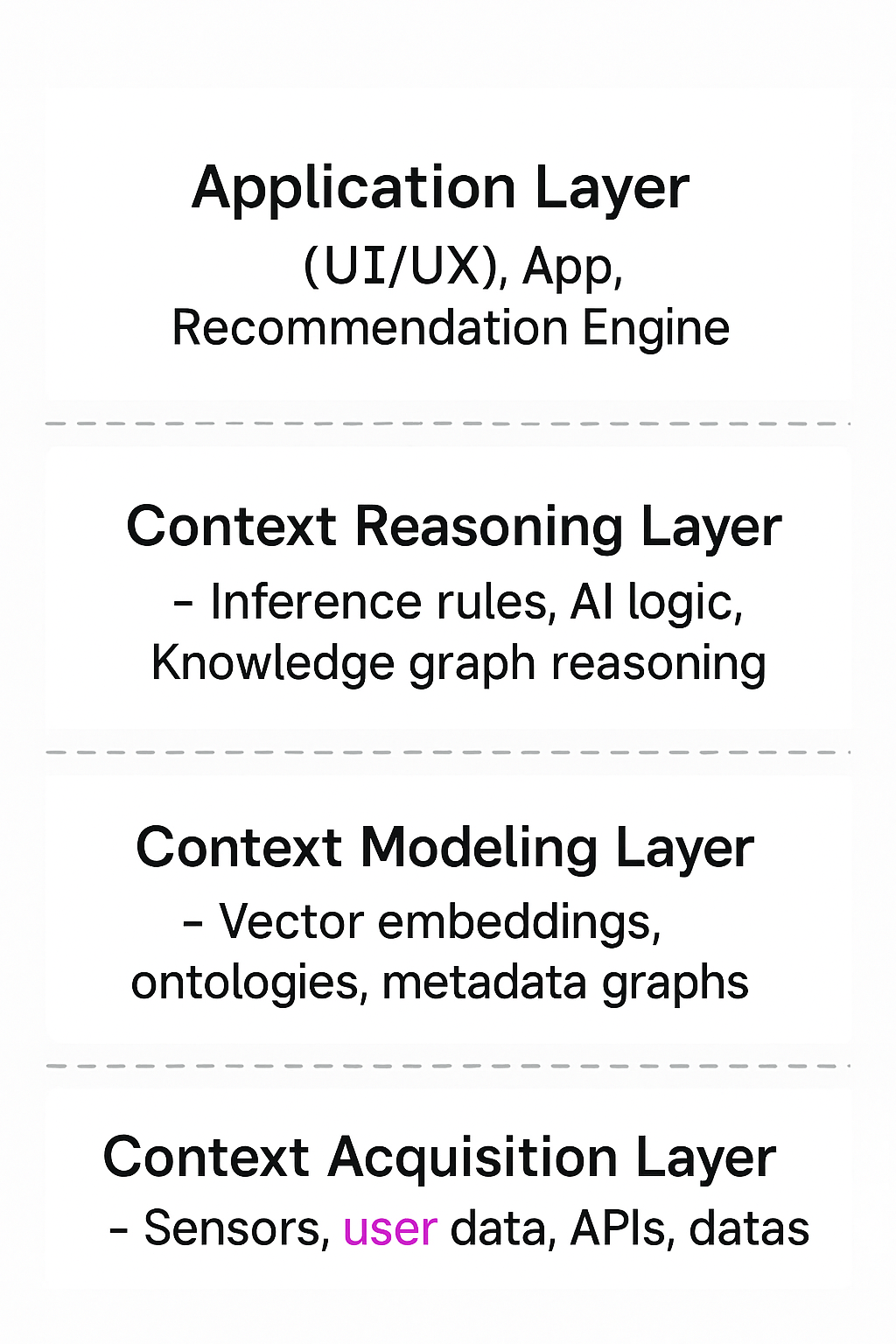
Each layer feeds into the next — from capturing data → modeling relationships → reasoning → delivering intelligent behavior.
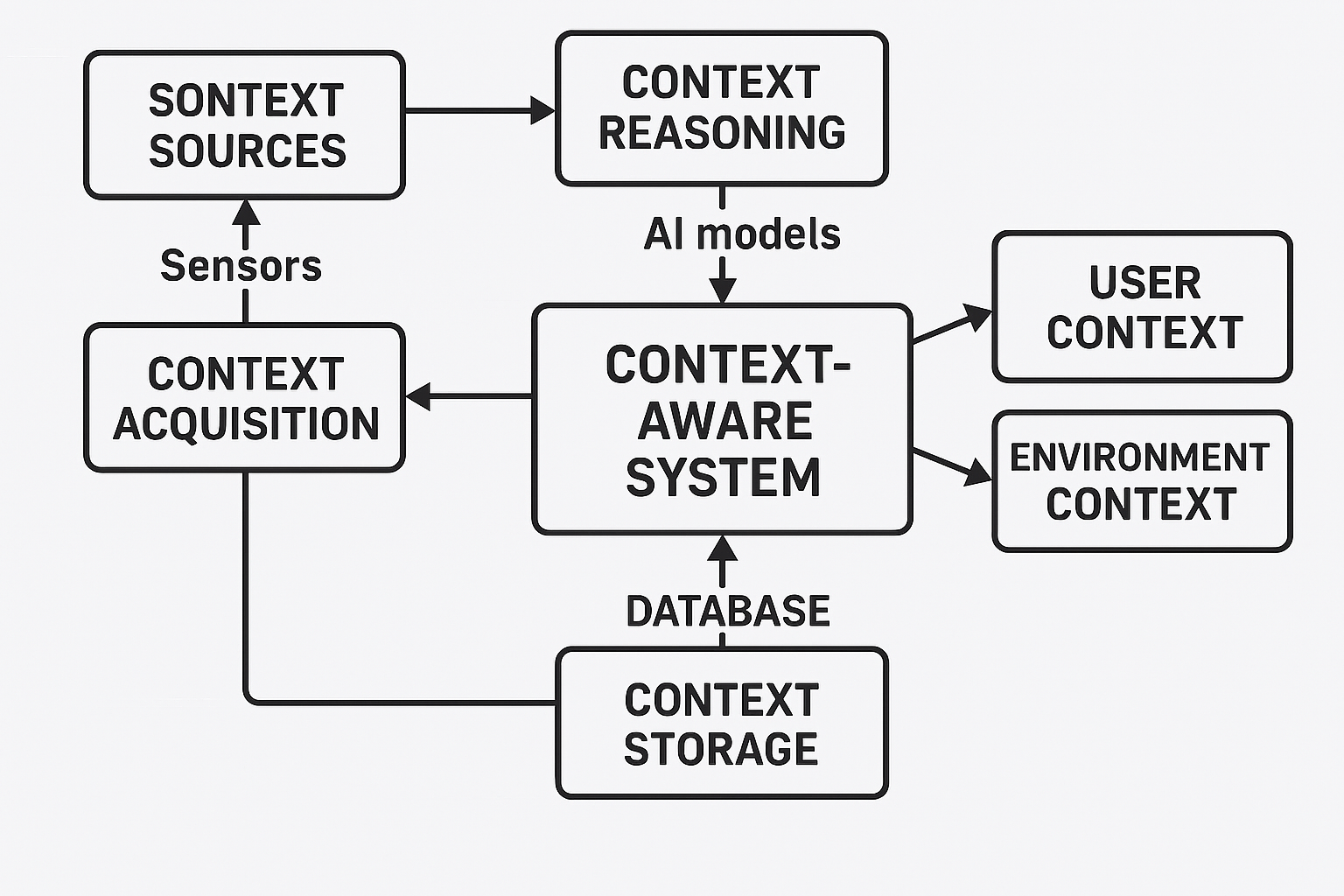
The following diagram shows various components of a context-aware system and their interactions.
🔍 Context Engineering in LLMs (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude)
In large language models, context defines how much information a model can "remember" or "consider" when generating a response.
This is determined by:
Context Window: The number of tokens a model can process.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Fetching relevant data dynamically.
Persistent Memory: Remembering user-specific data across sessions.
Session Context Graphs: Linking multi-turn interactions logically.
Example:
When you ask ChatGPT:
“What’s the follow-up on the proposal I mentioned earlier?”
It recalls previous context (“proposal”) from memory — that’s Context Engineering at work.
⚖️ Ethical & Privacy Considerations
Context Engineering involves managing user data responsibly. Key guidelines include:
Transparency: Inform users how their context is used.
Consent: Always collect contextual data ethically.
Security: Protect stored context (especially personal data).
Boundaries: Avoid overfitting or bias due to excessive personalization.
🔮 The Future of Context Engineering
Context Engineering will define the next wave of AI evolution — from reactive chatbots to proactive, adaptive digital companions.
Future Directions:
Multimodal Context: Merging text, voice, image, and sensor data.
Context Graphs for Agents: Shared memory between AI agents.
Long-Term Memory Systems: Context across months or years.
Context OS: Context as a fundamental part of operating systems.
Just as “data engineering” became essential for analytics,
“context engineering” will become essential for intelligence.
🧭 Summary
| Aspect | Context Engineering |
|---|
| Definition | Designing and managing the situational awareness of AI systems. |
| Goal | Make AI adaptive, personalized, and meaningful. |
| Key Components | Acquisition, Modeling, Reasoning, Management. |
| Difference from Prompting | Builds understanding instead of asking better questions. |
| Outcome | AI that knows you, learns you, and grows with you. |
✨ Final Thought
The real intelligence of AI won’t come from bigger models or longer prompts —
it will come from better context.
Context Engineering is how we move from smart chatbots to intelligent companions that truly understand the world around them.